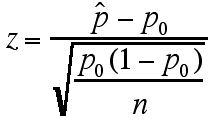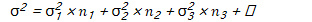Question 3
Z-score will not be changed after conversion
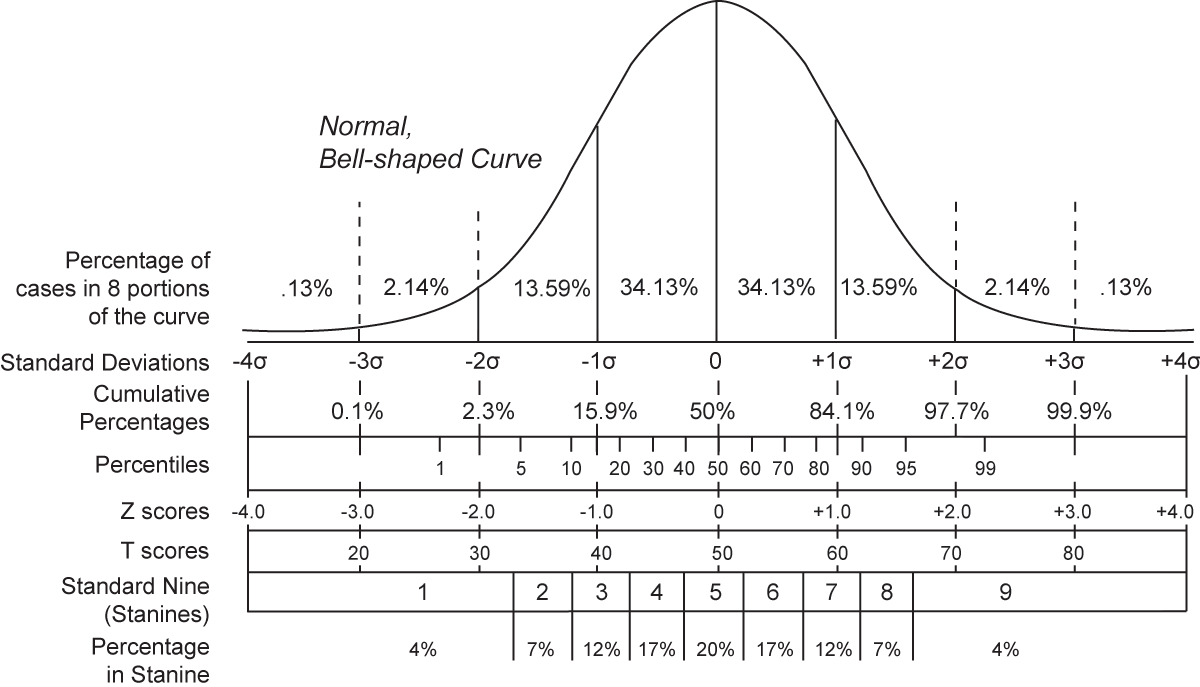
Question 13
Standard deviation of the sample distribution
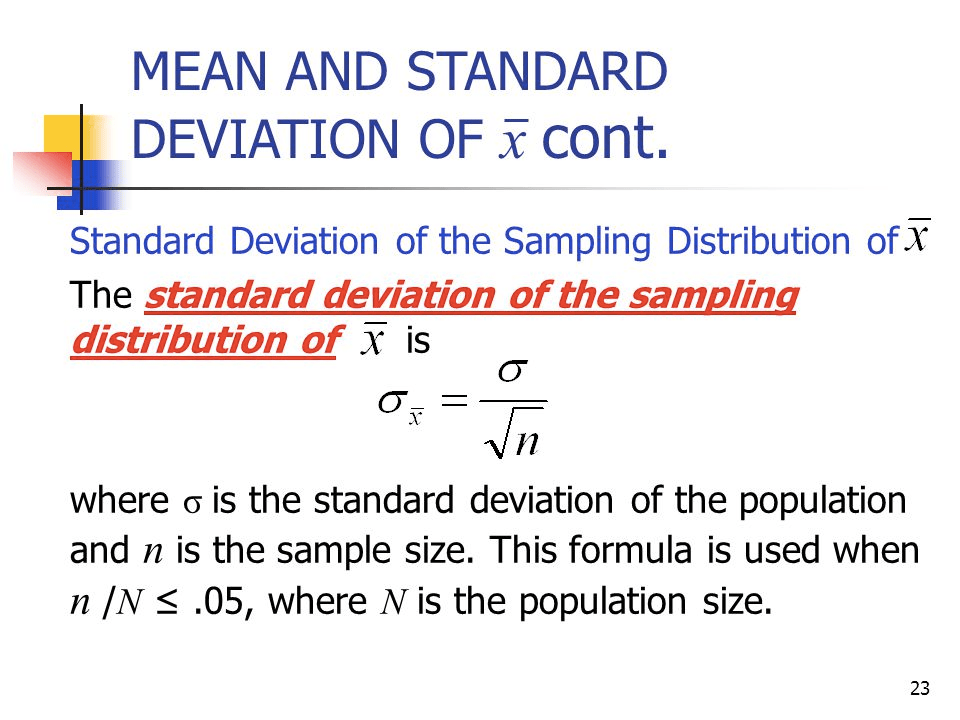
Standard deviation of the sample proportion
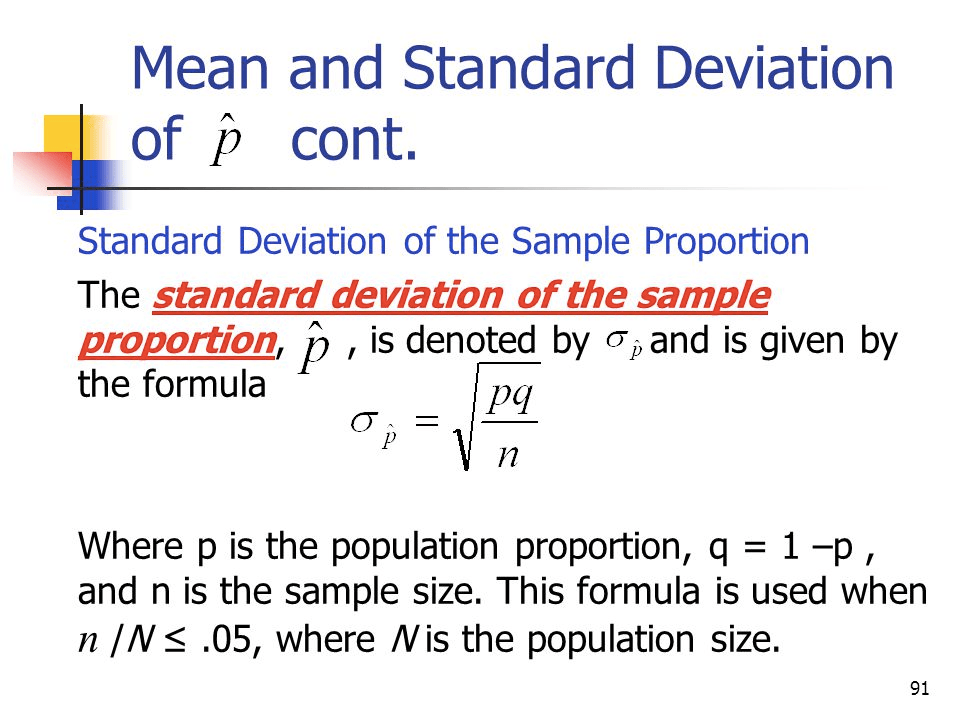
Question 20
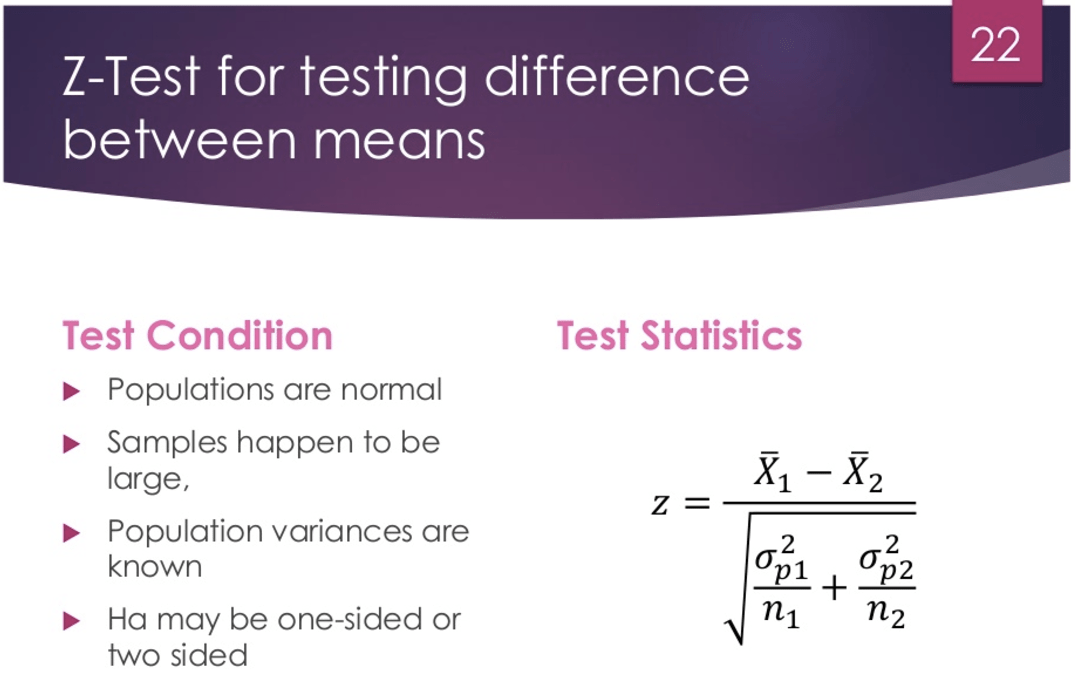
Question 20
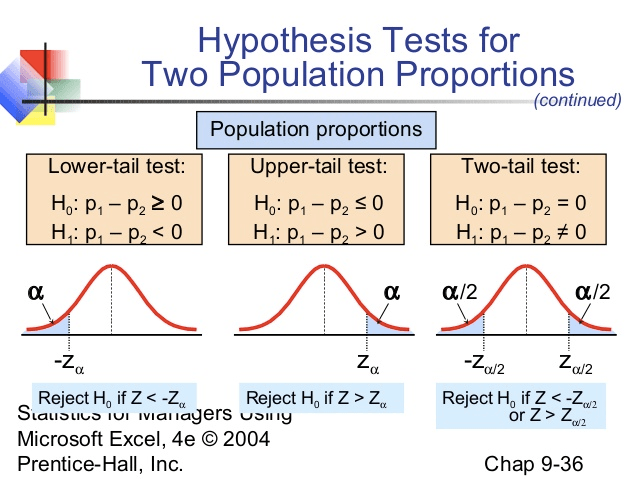
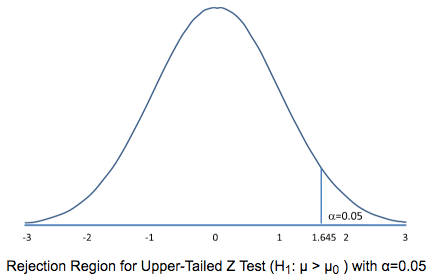
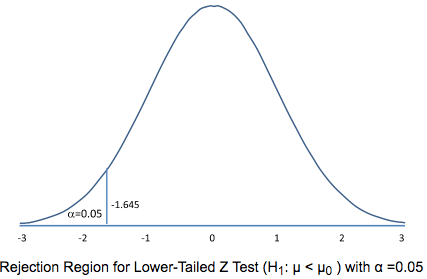
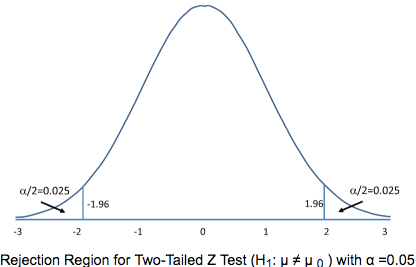
Question 23
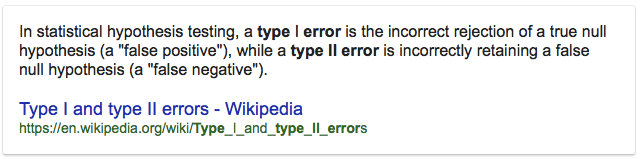
Question 24
Standard error of the difference
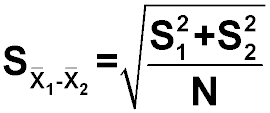
Question 28
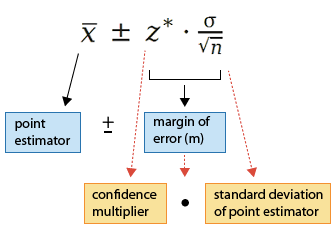

Question 32
Question 37